Although thousands of observations of diagnosis and subsequent treatment have been described, the disease has been studied.
The many diversity and nonspecificity of clinical pictures of pelvic varicose veins lead to serious errors in diagnosis, which can affect the consequences in the future.
Characterization of varicose veins in small pelvis
The veins in the pelvis are several times longer than the arteries, which determine their great abilities.This is due to the phylogenetic occurrence of the vascular system in the pelvic region.Veins in the pelvic are highly adaptable and may tend to reorganize, which helps to form dense interlaced networks.
The velocity and direction of blood flow are regulated by a valve, which is controlled by a complex humoral mechanism.Valve balances pressures at different parts of the venous network.
When the valve stops performing its function, blood stagnation can lead to pathology of blood vessels and the formation of varicose veins.The uniqueness of the veins of the small pelvis lies in the fact that the broad ligament of the uterus supports wide blood vessels, which may also be narrow, leading to pathology.
reason
Pathological dilation of the pelvic vein may be caused by:
- Violating blood outflow path;
- venous gun barrel prison;
- The changing location of the uterus (e.g., in repeated vitro) compresses the collateral trunk;
- Valve ovarian failure (congenital or acquired);
- obstructive postal syndrome;
- pathology of connective tissue;
- Arteriovenous vascular hyperplasia;
- Sitting for a long time, hard physical labor;
- Varicocele in the lower limbs;
- Pregnancy (3 or more) and delivery (2 or more);
- Diseases in the female reproductive area (chronic hermaphrodite, ovarian tumors, uterine fibroids and genital endometriosis);
- Adhesive process of pelvic organs;
- obesity.
Classified by disease degree
In terms of enlarged veins, the following degrees are distinguished:
- Up to 0.5 cm, "bottle opener" vascular stroke;
- 0.6-1 cm;
- More than 1 cm.
Choice of disease process
- Varicocele in the vaginal perineum and vestibular veins;
- venous whole blood syndrome in the pelvis;
symptom
- Most common - frequent pain in the lower abdomen, after long-term static and dynamic stress, the perineum.After the aggravation of hypothermia, fatigue, stress, and various diseases, the pain intensifies in the second phase of the cycle.
- This feeling is "not at ease", sexuality and subsequent pain.
- Dysmenorrhea - Menstrual diseases, including pain syndrome.
- Secretes more than normal reproductive tract gallbladder.
- Blood stagnation leads to infertility, incompetence, and termination of pregnancy.
- Urination is violated due to the swelling of the bladder vein.
diagnosis
In only 10% of cases, the diagnosis of the disease is successful only through complaints.
Palpation of the inner wall of the pelvic wall makes it feel the rectangular seal and the nodes of the veins.When examined in a mirror, cyanide in the mucosa of the vagina can be seen.
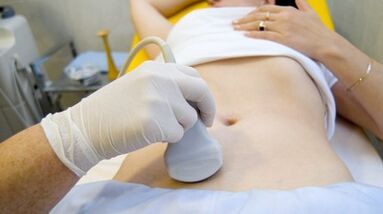
The process of selection is an ultrasound study with color Doppler mapping that not only identify varicose veins in the ovarian vein, but also identify venous thrombosis, post-ossification occlusion after botulinum ossification.Using ultrasound, it can be seen that the "worm", the structure of signal reflection, is located on the lateral side of the uterus.
The effects of the Doppler study are based on the “coloring” of blue and red, venous and arterial blood, correspondingly.
Devices that use special procedures for ultrasound examination recognize the sensor and blood movement in the other direction, calculate blood flow velocity and blood vessel type.
However, the exact definition of a vein is the artery behind the doctor.The Doppler method works in almost all cases, and our bodies determine the exception to the rules, because the blood flowing from the heart is not always the artery and vice versa.
Therefore, ultrasound diagnosis doctors see arterial or venous blood vessels, their size, blood flow, and many indicators that ordinary people do not need, but rather play an important role in the diagnosis.To do this, use abdominal and transvaginal sensors.
In 5.7% of cases, the disease was accidentally identified during screening.Typically, the diameter of the ovaries is 0.4 cm.
CT and MRI are very accurate.Using these methods, you can find accumulation of varicose veins around the uterus, ovaries, and these organs.The accompanying pathology can be determined.
A very reliable approach is a venologic study.
Contrast was compared with blood flow at the height of Valsalva samples.This allows you to see the valve failure.
Adrenoscopy on the left side, renal venoscopy, super-sequence venoscopy and venoscopy on both sides were also used.These methods allow you to determine blood and anatomical changes in the renal vein and where it falls into it.
Superbacteria scopic examination is performed by gonadovenous catheterization through femoral antonyms or subclavian veins, followed by contrast.
Most of the blood in the varicose veins is thrown away by the ovarian veins.But under high blood pressure, it enters the internal vein through the non-protruding uterine veins.Outflow can pass through outflowed venous plexus, including the s bones and plexus of the bladder.
Color on the left
- The plexus of the left ovary does not flow out or proceeds along an additional short circuit.
- There is still a long journey.
- Two additional outflow paths or another auxiliary path can be seen.
In stages 2 and 3, varicose veins formed in the right ovarian tuft.
Laparoscopy is used for differential diagnosis.The pathologically tortuous veins are in the ovaries, towards the direction of the circular and wide ligaments.They look like large blue conglomerates with thin and tense walls on them.
The complexity of diagnosis is that the disease is often hidden behind signs of the inflammatory process, citing clinical manifestations, in endometriosis, prolapse of the visceral viscera, postoperative neuropathy and many extragenic diseases.
treat
The main purpose of treatment is to remove reflux from the vein.In the early stages of the disease, conservative treatment was used.In the later stages of the disease, the treatment chosen is surgery.
Conservative treatment
It includes normalizing vein tension, improving hemodynamics and nutritional processes.
Symptom-related treatment to eliminate individual symptoms.NSAIDs Anti-inflammatory Pain, Bleeding - Hemostatic Treatment.
The main drugs in conservative treatment are poisons and anti-white blood.
Alveolar - Improves the tone of the blood vessel walls and enhances blood flow.With this disease, it is best to consult a gynecologist for certain medications.
One important approach is physical therapy practice.
Surgical treatment
- Reviving varicose veins.
- Gondo-Kavari diversion.
- Sclerotic laparoscopy sclerosis.
- Occrame of ovarian veins using X-ray-intravascular approach.
Folk therapy
Since the main factor in the occurrence of this disease is the weakness of the valve device, this pathology is also used in all folk remedies for varicose veins in the lower limbs.
Most commonly used are: regular hazel, hops, nettles, horse chestnuts, dandelion roots, tea mushrooms, willow, oak, St. John's wort, a range, pollen and more plants.
Effective IS: Treatment with oak bath, chestnuts, willow, chamomile, pharmacy, dry herbs, St. John's wort.
prevention
- If the complaint, predictors or illness listed above are listed, please contact your gynecologist.
- It is necessary to normalize the working state and rest, and try not to maintain an upright position for a long time and to adapt to the body.
- Practice for prevention of "pedal", "stand stack", and "foot legs"
- Follow the diet: Eat foods that are high in vitamins E, R, C, try to eat only white meat, reduce fat, and replace it with fruits, vegetables, and grains.
- Drink enough liquid, but no less than 1.5 liters per day.
- Get rid of too much weight and bad habits.
- Consult the attending physician, which involves wearing compressed linen, which will improve blood flow from the lower limbs, thus stagnating in the pelvis.
- Avoid baths, saunas, steam baths, hot baths.
In order not to get sick with such a difficult disease, it is necessary to follow the prevention recommendations listed above.Think of your health as the most valuable in life.
There are slightest suspicious symptoms you can't get rid of for a few days, and you should consult your doctor.He must provide you with high-quality help and save you from pain.